What are the Newest Hospital Technologies?
The healthcare industry is ripe for some major changes. From patient care and treatment to research and marketing, there are endless opportunities to use technology to deliver more accurate, efficient, and quick interventions at the right moment in a patient’s care. Here are some of the newest hospital technologies and their uses.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the newest hospital technologies today. It is becoming more sophisticated at doing what humans do, but in a precise, quick and affordable way. AI can help in medical diagnosis, mental and behavioral health, medical marketing, human resource management and more.

Hospitals are now using AI in HR management to streamline workflows. This will allow health care providers to serve maximum patients on any given day without compromising quality. Hospitals are also integrating AI systems to the workflow and scheduling software to allow for real-time adjustments whenever appointments and cancelations come in.
In addition to optimizing workflows, AI is also helping in-clinic decision support systems. It uses electronic health data to get a decision-making outline for enhancing the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of different illnesses based on treatment history patterns, health, and demographics.
AI is also widely used in:
- Medical marketing, to help facilities effectively compete for patients
- Expanding access to care in developing or underserved regions
- Development of the next generation of radiology tools
- Containing the use of antibiotic resistance
- Advancing the use of immunotherapy for cancer treatment
- Creating more precise analytics for pathology images
- Monitoring health through personal and wearable medical devices
Robotic technology
Robotics, like AI, is quickly changing the healthcare landscape. While the history of robots in healthcare dates back to 1985, there have been massive improvements in the area. Thanks to advances in sensor and motion control technologies, robots are way more autonomous and precise than in the age of PUMA 200. They are not only capable of helping but performing complex surgeries themselves.
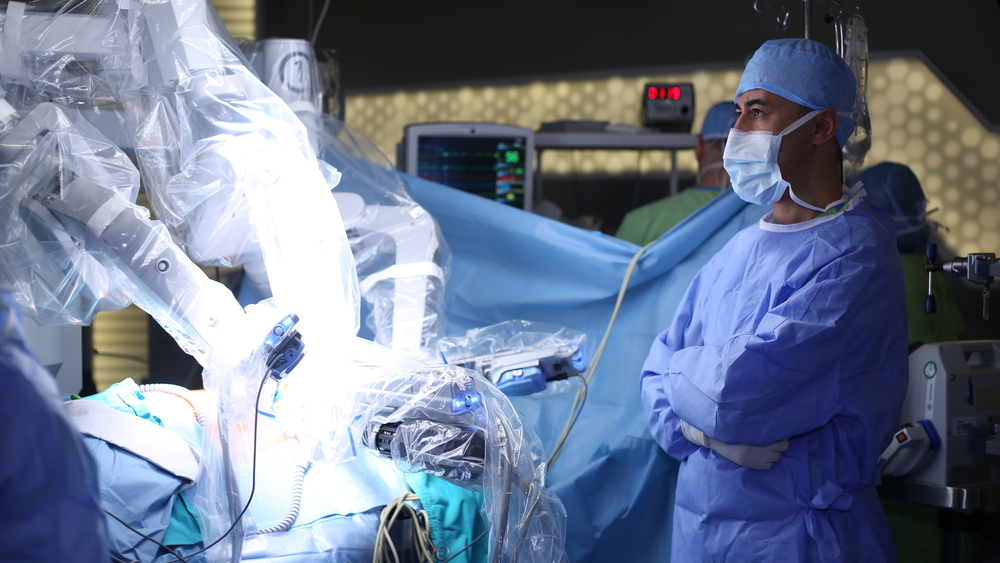
The integration of robots into healthcare operations offers a range of benefits:
- Provide help and comfort to patients and visitors
- Eliminates human error in high-risk yet delicate procedures
- Improves patient recovery time
- Makes personalized and targeted treatments
- Reduces the time needed for surgeries
- Shortens hospital stay
Robots are widely used in orthopedics and surgery. In 2019, a surgeon leveraged robotics and 5G internet to perform remote surgery on the brain of a Parkinson’s patient who was nearly 1,900 miles away.
This new technology plays a vital role in creating new care models for the growing senior population. It also solves the challenge of delivering quality solutions to new and underserved markets. In both cases, robotics helps facilities to cut down costs. And the best part is that the current robotic systems are pretty impressive. Surgeons can do more operations in comparable time as before, but with higher success rates.
Blockchain
Blockchain is one of the newest and most important technologies in the world. It is a time-stamped series of unchangeable records of information managed by a network of computers instead of a centralized authority.
Blockchain has extensive uses and applications in healthcare:
- Manages the medicine supply chain
- Facilitates the secure transfer of patient medical records
- Helps medical researchers to unlock genetic code
- Eliminates breaches in doctor-patient confidentiality
- Prevents medical errors
- Helps reduce healthcare costs
- Improves research in medicine
Ledger technology can also help manage and prevent future pandemics. This is especially critical, considering how COVID-19 has put the healthcare system to its greatest test of the century. Healthcare systems have had a challenge storing and circulating data in real-time. But now, the CDC in collaboration with IBM and WHO is set to use blockchain to monitor, store, and distribute sensitive data in real-time to facilities for effective and uniform management of the virus.
Other common uses of blockchain technology in healthcare include ownership and security of digital assets, fixing digital display advertising and changing data collections.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
IoMT refers to all medical devices and applications that can connect to the health care data technology system using the internet. The technology facilitates the transition from reactive-to-preventative patient-oriented care.
The IoMT sector is fast-growing and has multiple innovations underway. From patient diagnostic machines to smart monitors, radical solutions are being created to take care of the health care challenges.

According to Deloitte, the IoMT market is projected to hit the $158.1 billion mark in 2022. Some common uses of IoMT include:
- Real-time patient monitoring
- Fitness tracking and diagnostics
- Ingestible cameras and sensors
- Smart and continuous glucose monitoring
- Asset monitoring and maintenance
- Creation of powerful EHR systems
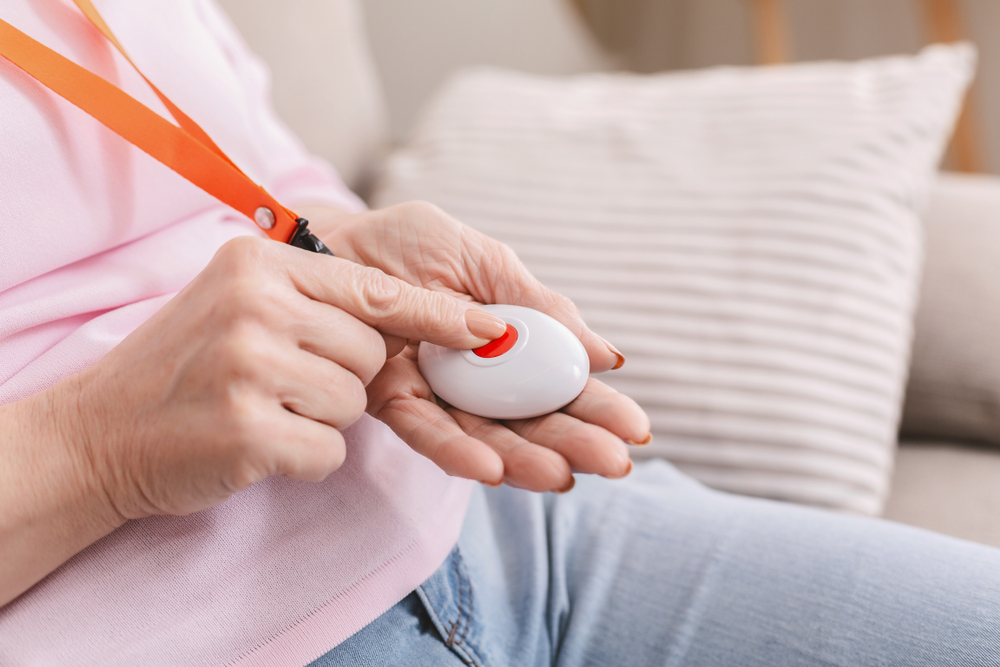
- Personal emergency response
- Virtual home systems.
Virtual reality and Augmented Reality
From improving the patient experience to changing the way medical students learn, these new technologies transform the way things are done in hospitals. Virtual and augmented reality technologies have the potential to make surgical planning easier. Even the most experienced surgeon may come across surprises when performing surgery. But virtual reality and augmented reality may make those instances less common.
The ability to see the inside of the human body in VR is useful to patients and doctors alike. VR allows surgeons to educate patients about their surgical plan. This enhances the understanding of treatment, leading to more patient satisfaction.
Additionally, VR has the unique ability to transport patients to an entirely different place. So, doctors use it to create robust simulations of scenarios where psychological difficulties happen. This cuts out the need for therapists to accompany patients on a trip to a tall building or market place for real-life situations. Other AR/VR uses include:
- Pain management and physical therapy
- Medical marketing
- Disease awareness
- Evaluating medication dose distribution in 3D
Personalized mobile applications
Mobile apps are not only great for patient engagement but monitoring and treatment as well. There are vast patient scenarios that use mobile apps in 2020. For instance, one can schedule appointments, check-in, upload medical records, or even get test results through apps.

Apps help hospitals reduce operational costs, thanks to their ability to relieve some pressure on caregivers, receptionist duties and waiting times. Other common uses of apps include communication and healthcare marketing – helping hospitals get in front of customers. And with the widespread use of mobile devices, app use is only set to increase in the coming years.
Precision medicine
Precision medicine is a new hospital technology that allows doctors to select therapies and medicines to treat patients based on their medical and genetic make-up. Personalization makes treatment more effective. It attacks problem areas (like tumors) based on the patient’s specific proteins and genes. This makes it easy for cancer to be destroyed by treatment.
Other than cancer treatment, precision medicine is also effective in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It uses the same mechanism to destroy RA's vulnerable genes, weakening the disease and reducing symptoms.
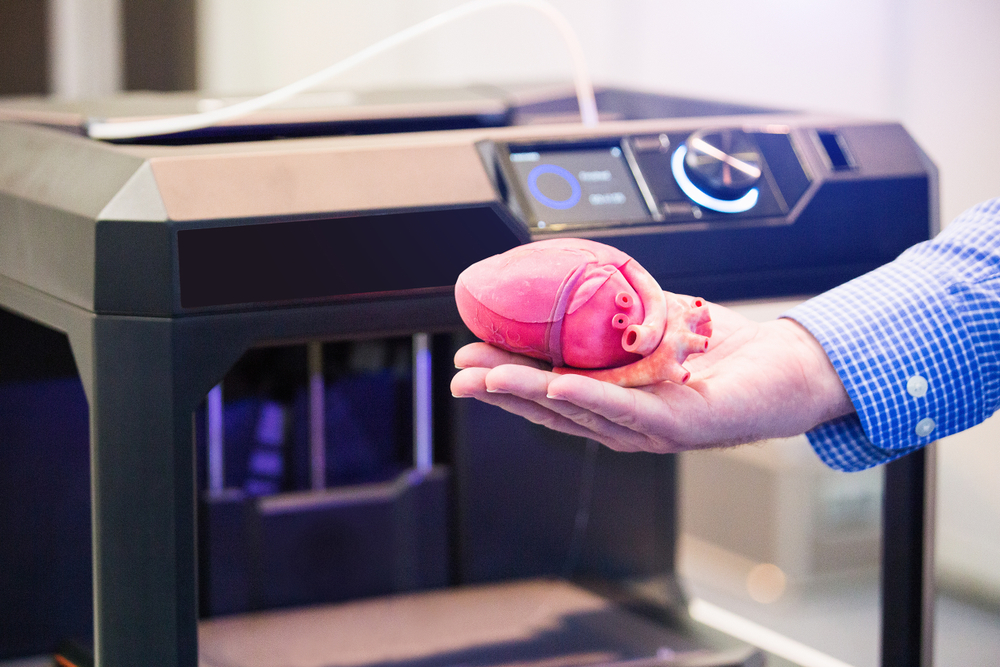
3D printing
3D printers are among the newest technologies on the market today. Experts use these printers to create implants and joints used in surgeries. 3D prosthetics are especially popular, thanks to their unprecedented levels of comfort and mobility. These solutions are usually highly personalized, thus match up the patient’s exact measurements. Other uses of 3D printing in healthcare include printing pills containing multiple drugs and even creating human cells and tissue.

Frank is a technology visionary and strategic hands-on executive with over 20+ year track record of helping companies revitalize, restructure, and implement complete Unified Communications systems in national and global markets.