What is the Future of Nursing Home Businesses?
The Coronavirus has changed the way we do things, albeit temporarily. Soon enough, things will settle down and life will pretty much go back to the way it used to be – at least for other industries. The senior care industry, however, may never return to the old normal. With that being said, what is the future of nursing home business going to be like?
The COVID-19 pandemic has dealt significant blows to the senior care industry. According to an ABC News analysis of the latest public health data, nursing homes in America have persisted as one of the pandemic's deadliest environments. As of May 31, 2020, there were a total of 95,515 confirmed and 58,288 suspected cases of COVID-19 in 88% of 15,400 Medicare and Medicaid eligible nursing homes. Of this number, 31,782 succumbed to COVID related complications.
Today, many nursing homes across the US remain on lockdown. The devastation, advocates and experts say, underscore longstanding problems with a system that, even in normal times, struggles with neglect, poor infection control, and understaffing. Now, the pandemic has fuelled calls for more drastic solutions, some have called for abolishing nursing homes altogether.
Advocates question the need for nursing homes, especially since many believe seniors aren't receiving proper care in these facilities. Their effort to deinstitutionalize nursing homes – which has had some success – pushes for in-community and home care options for disabled adults who need long-term care.
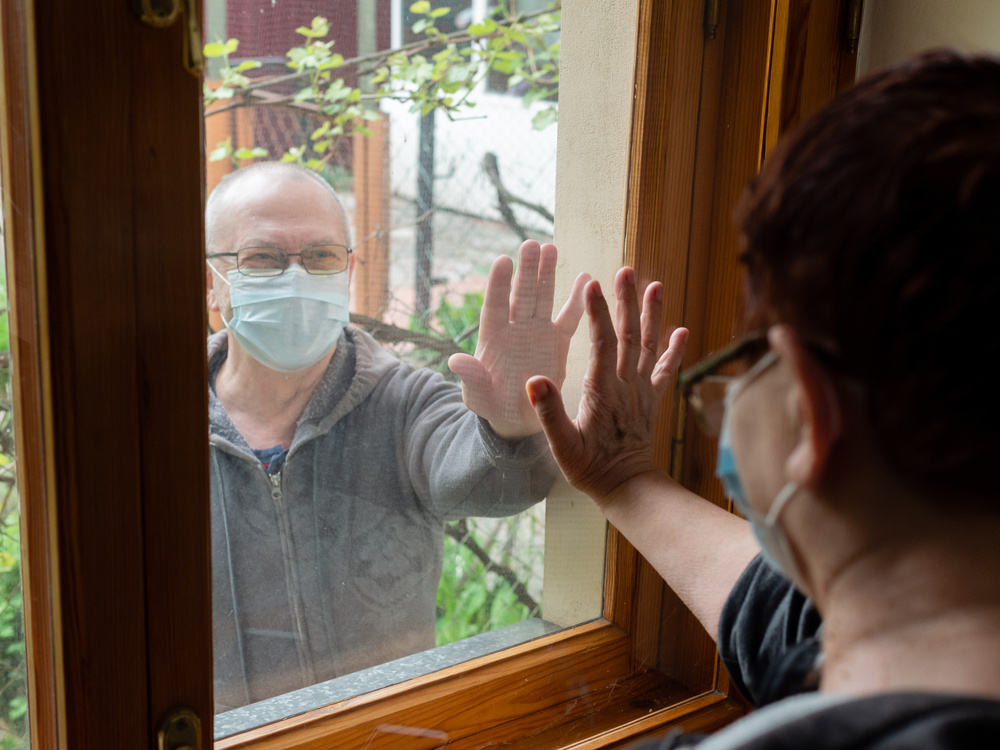

But the pandemic isn't the only problem facing the senior care industry. There are also some daunting economic and policy challenges that arise due to the growing baby boomer population. Again, many facilities were struggling with thin profit margins before the pandemic. Others were struggling to offer quality care or to stay afloat, and so on.
Of course, with all these things happening in the senior care industry, it only makes sense to wonder what the future holds for the nursing home business. This is especially true if you are considering investing in the industry. In this article, we will dive deeper into what's happening now and what the future looks like to give you an idea of what to expect.
What is a nursing home?
A nursing home is a place where those who don't need to be in a hospital but can't access home care go. Most of these nursing homes have skilled nurses and aides on hand 24 hours a day. They offer custodial care, like helping the elderly get in and out of bed, bathing, dressing, and even feeding. They also provide skilled nursing services like medical monitoring and treatment to improve older people's quality of life.
Estimates indicate that the number of Americans aged 65 and older will almost double from 52 million to 95 million between 2018 and 2060. By this time, the older adults will account for 23% of the population. With more seniors living longer than ever before, there has been a rise in the number of seniors needing nursing home or assisted living care. This explains why investing in senior living facilities is a good idea - but with a catch.
The state of nursing home business today
Nursing homes fulfill a need that is never going to go away – caring for the elderly. For as long as there are seniors, there will be facilities to help cater to their needs. But as we mentioned earlier, the pandemic has exposed the inherent flaws in these homes. Up until now, the country is still struggling to contain the outbreak. So we may not be in the best position to predict the actual backlash and the regulations that will be in place to ensure that these facilities are well prepared to handle any infectious disease outbreak in the future.
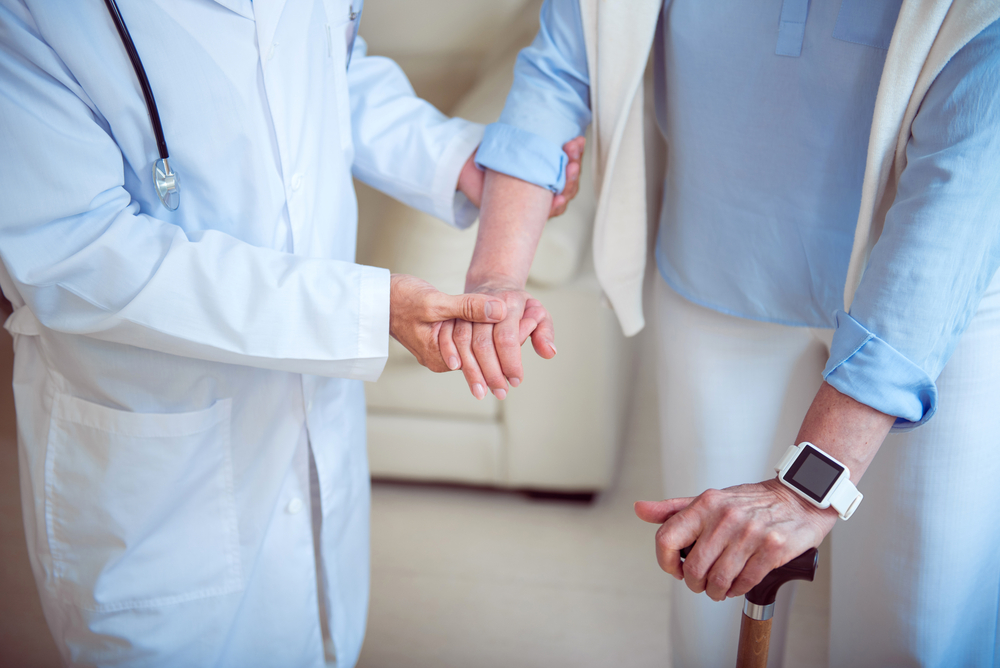

As we mentioned earlier, many nursing homes were struggling with thin profit margins before the pandemic. But now, they have to spend more money on protective equipment and technology to connect residents with loved ones who can no longer visit. They also have to redesign their spaces to optimize infection control, and for some, this may mean losing beds. Add that to the rising demand to increase staff and pay, and it becomes expensive for these facilities to operate efficiently.
The revenues have also gone down because facilities are only enrolling a few residents to reduce the risk of infection. This spreads the already thin profit margins even further, making it hard for some to pay bills without government help. And even with government programs like Medicaid, operators still have a hard time because these payments don't always match up with care costs.
The future of nursing home business
Nursing homes play an essential role today, as they will in the coming days. Many seniors stay in these facilities because of various reasons. Some have an underlying health care problem that needs skilled hands. Others don't have a family member close by to help with daily tasks. But the trend is quickly changing as more families and their elderly loved ones start to opt for in-home care.
According to one report, residents are moving out of senior living homes faster than those moving in. Seniors and their loved ones are responding to at least three trends:
- The risk of Coronavirus in nursing homes
- High costs associated with nursing homes, especially when many are struggling financially
- The inability of family members to visit (or the restrictions to see a loved one)
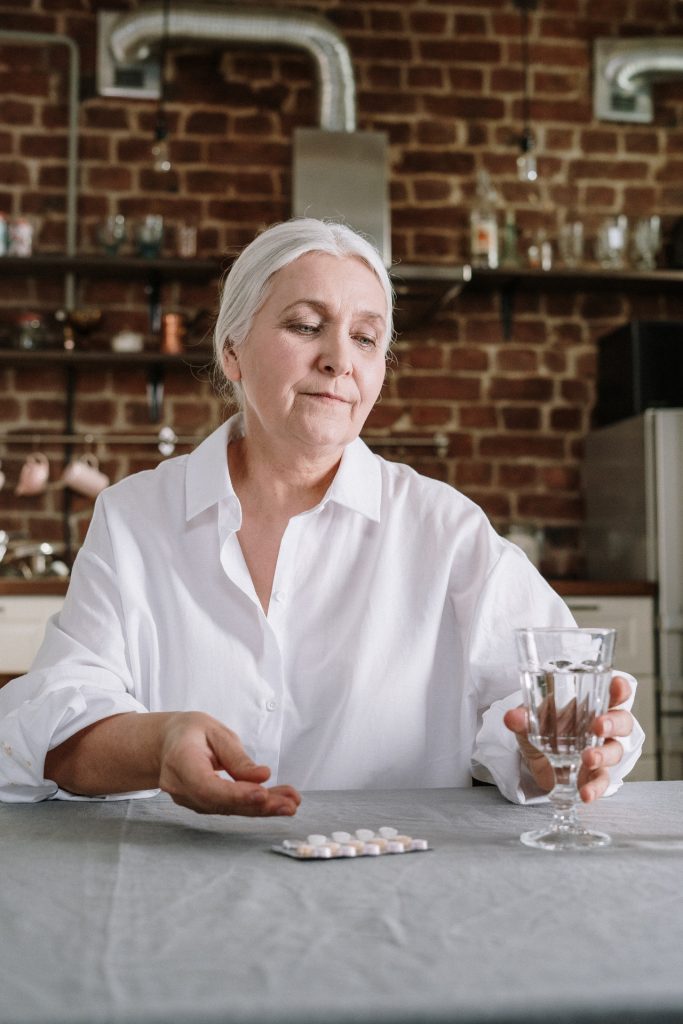

This shift to home care will see many people embrace vast health care technologies to monitor and care for their loved ones at home. The Internet of medical things is widespread today. It allows people to do a range of things, including monitoring vital signs, routine tests, exercise, and even sending alerts in case of an issue. A good example is a wearable device that lets senior adults monitor their heart rate, sugar levels, and so on. Such tools allow older adults to send real-time medical alerts, making it easier to receive timely care. Motion sensors are another excellent example of modern care technology that's transforming the senior care world.
Owing to these trends, analysts predict that the nursing home sector will see a massive ownership shakeout, with some even going out of business because of the thinning of profits. There's a bit of conflict, though, as to whether this will lead to a net decline in beds or ownership consolidation – or both.
While the pandemic did not create the challenges facing nursing homes, it did expose them in a “not so good” way. Both federal and state governments made steps to help weather the storm; as the pandemic's depth became more evident, the federal government polished its policies and increased resources for facilities and states. The makers of policies should now review the entire strategy to see what works and what should be included in the long-term systemic change. All of this will greatly affect the future of nursing home business.
With an increasing elderly population and looming state budget cuts, the system is at risk of continued deterioration – including limited oversight, less access to essential services, and worsening of the understaffing situation. The pandemic placed the system on trial and despite all the effort to keep everything afloat, that system failed. Whether the system will stand the test of time or not is all dependent on responsible parties to make bold and lasting changes.

Sheri Bruemmer is a seasoned industry expert with expertise in growing and managing operations that support assisted living, adult foster care, and homes for the aged communities. Sheri is a certified Gerontologist, licensed Assisted Living Director, and licensed nurse as well.