Why is Remote Patient Monitoring Important?
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is changing the healthcare landscape for the better. Today, patients don't have to leave their homes to access different healthcare services. In fact, they can sip coffee in their backyard while their smartphone and wearable devices report vital signs like heart rate, dietary intake, blood sugar levels, etc., to their care team. Doctors, too, can monitor their patients remotely and ensure they adhere to their treatment regime.
That is RPM and chronic care management at its best - no traffic, crowds, waiting times, extra cost, stress, etc. Smartphones and wearable devices allow medical systems to offer remote care for relaxed, engaged patients while real-time health data, like beats per minute, is sent to the care team.
Years of studies and documentation by many experts including federal government officials have shown that remote patient monitoring (RPM) can improve patient outcomes for those suffering from chronic conditions like heart failure, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and COPD. According to these studies, remote patient monitoring is among the most effective and efficient tools for chronic disease management for seniors, especially those with these diseases.
What is remote patient monitoring?
RPM uses digital technologies to track and capture patient’s health data and transmit the data to providers for assessment and, when necessary, instructions and recommendations. It allows medical providers to monitor real-time changes in patient’s data remotely once they’re discharged from the hospital. RPM is a critical part of the wider telehealth industry and eHealth domain.
Remote patient monitoring focuses on patients with chronic diseases or in rural areas with limited access to hospitals. Providers also use it to monitor senior and post-operative patients.
According to studies, RPM can:
- Reduce readmissions by 38%
- Improve patient satisfaction by 25%
- Reduce emergency room visits by 25%
- Reduce the cost of care by 17%
- Improve medication compliance by 13%
With RPM, healthcare providers can monitor patients in their homes, on vacation, at work, etc., using monitoring devices like:
- A pulse oximeter to measure pulse and wavelengths that determine blood oxygen levels
- Portable ECG devices to detect life-threatening conditions like arrhythmia, ST depression, myocardial ischemia, or even drug toxicities and cardiac chamber abnormalities.
- Medical alert systems to detect falls among older adults, age 65 and older, as they’re at at a high risk of falling.
- Continuous glucose monitoring for managing diabetes effectively.
- Blood pressure cuff calculates the patient's blood flow and heart rate. It can also help in the early detection of conditions like kidney dysfunction and diabetes for better outcomes.
- Anticoagulation testing devices for continuous blood testing in patients with artificial heart valves, fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, or deep vein thrombosis
- Heart rate monitors measure heartbeats per minute during sleep, exercise, errands, or stressful events.
- Smart scale for patients managing congestive heart failure, obesity, and so on
The importance of remote patient monitoring
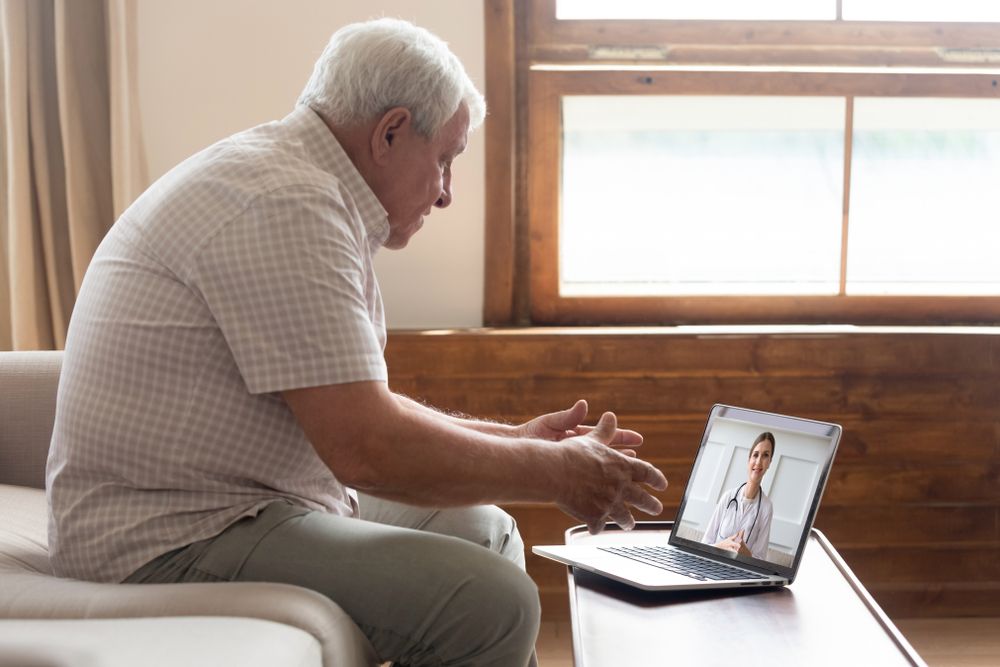

Enhances doctor-patient communication
Communication between patient and doctor is critical in healing and recovery. Remote patient monitoring facilitates communication and forges transparency and trust. It offers a deeper understanding of conditions and treatment, enabling patients to take more control of their care plans.
It helps physicians overcome burnout
Burnout is a real issue in healthcare. According to a Medscape survey before COVID-19, about 50% of doctors experienced burnout. A follow-up survey in September 2020 found that 64% had more intense burnout than before the pandemic.
Many cited time pressures and performing delicate procedures in chaotic environments as the leading stressors. Uncertain patient outcomes and overcrowded, understaffed health facilities were also cited.
Remote patient monitoring allows medical providers to perform routine patient care without physical visits to the hospital or clinic. This redirects resources and space from “healthy” patients to those with acute medical attention. As a result, it eases the strain on the system and the stress on doctors - thereby reducing burnout.
Reduces the risk of infection at hospitals
Since RPM is all about monitoring patients virtually, doctors can keep sick people from their offices. This keeps healthy people out of harm's way, especially in a health crisis such as the COVID-19. Patients with acute or chronic diseases that can be managed at home can use RPM. This way, they don't have to make unnecessary trips to the office and expose themselves to infections.
It helps healthcare facilities to grow
Buying medical software and equipment is a significant investment upfront. But RPM pays over time both in terms of growing the practice and offering better patient outcomes. With RPM opened to many Medicare and Medicaid patients, an investment in the opportunity is a good long-term strategy. Experts say this could become the new standard, and patients may start to expect their insurance company to support RPM.
Ensures patients get personal, proactive care
Remote patient monitoring is proactive care. It tracks the patient’s vitals, performs disease-specific analysis, and answers health questions while keeping the care team advised. Patients enjoy better service for their health problems, and providers get to monitor health patterns and detect treatable issues before they escalate into emergencies.
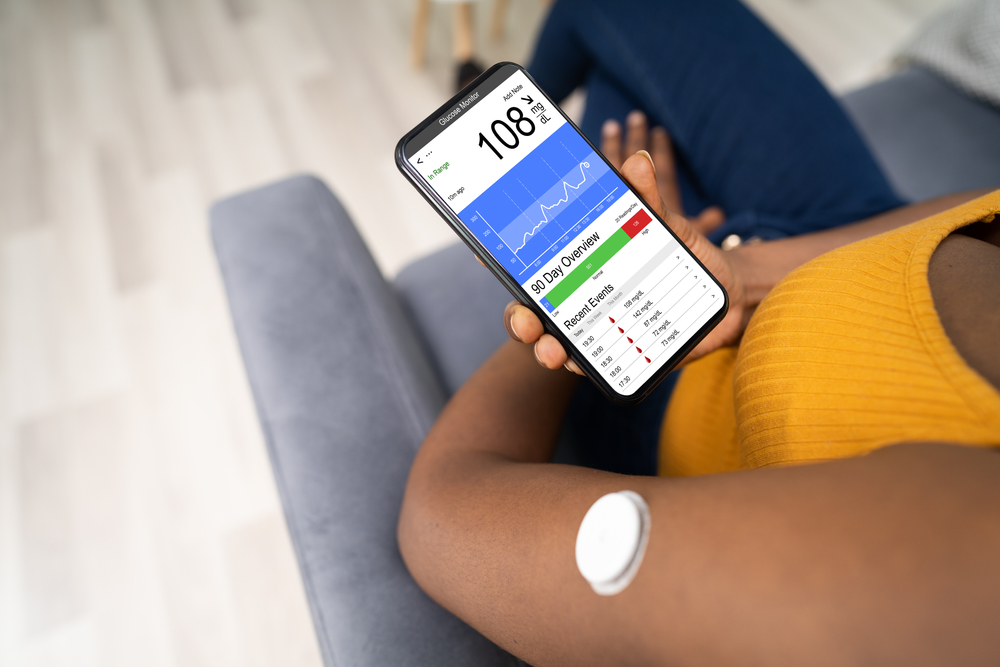

It optimizes time spent with patients
With remote patient monitoring technology, providers need not spend time measuring vitals and asking questions. That’s because they already have the patient data at hand. So, in-person meetings are spent answering questions and making the most out of the time. And when providers have fewer tasks, they are less likely to burn out.
For instance, devices like smart scale detect water retention in patients managing congestive heart failure. Any changes might prompt the physician to prescribe a diuretic, increase the dosage, or call the patient in for a visit.
Offers cost savings and reduced hospitalization
RPM has the potential to minimize hospitalization and readmissions as it allows caregivers to monitor patients remotely. This reduces costs for both patients and healthcare systems. It also increases Medicare coverage reimbursement rates and helps hospitals improve their industry reputation.
According to one report, widespread adoption of RPM could save the US as much as $6 billion annually. RPM helps deal with age-related health issues, which account for nearly 90% of US healthcare costs. That’s because it allows care to be moved out of hospitals into homes. When facilities cut on costs, the savings trickle down to patients.
Improves patient outcomes
Possibilities with remote patient monitoring are diverse. The technologies can detect out-of-range values that can be alarming and identify trends that point to the need for changing care plans. They also offer coaching on everyday choices like exercise that tend to be ignored despite their significance on chronic condition management. Patient support ensures a better quality of care and can improve outcomes.

John is a highly respected and seasoned C-level sales, operations and general management executive, with decades of proven success in growing sales and profits while vastly improving operational disciplines.